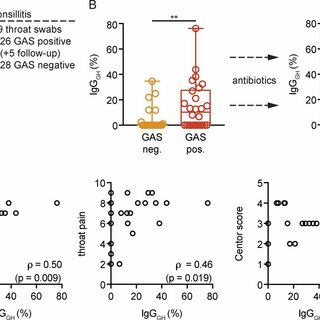
Delayed booster dosing improves human antigen-specific Ig and B
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
medRxiv - The Preprint Server for Health Sciences
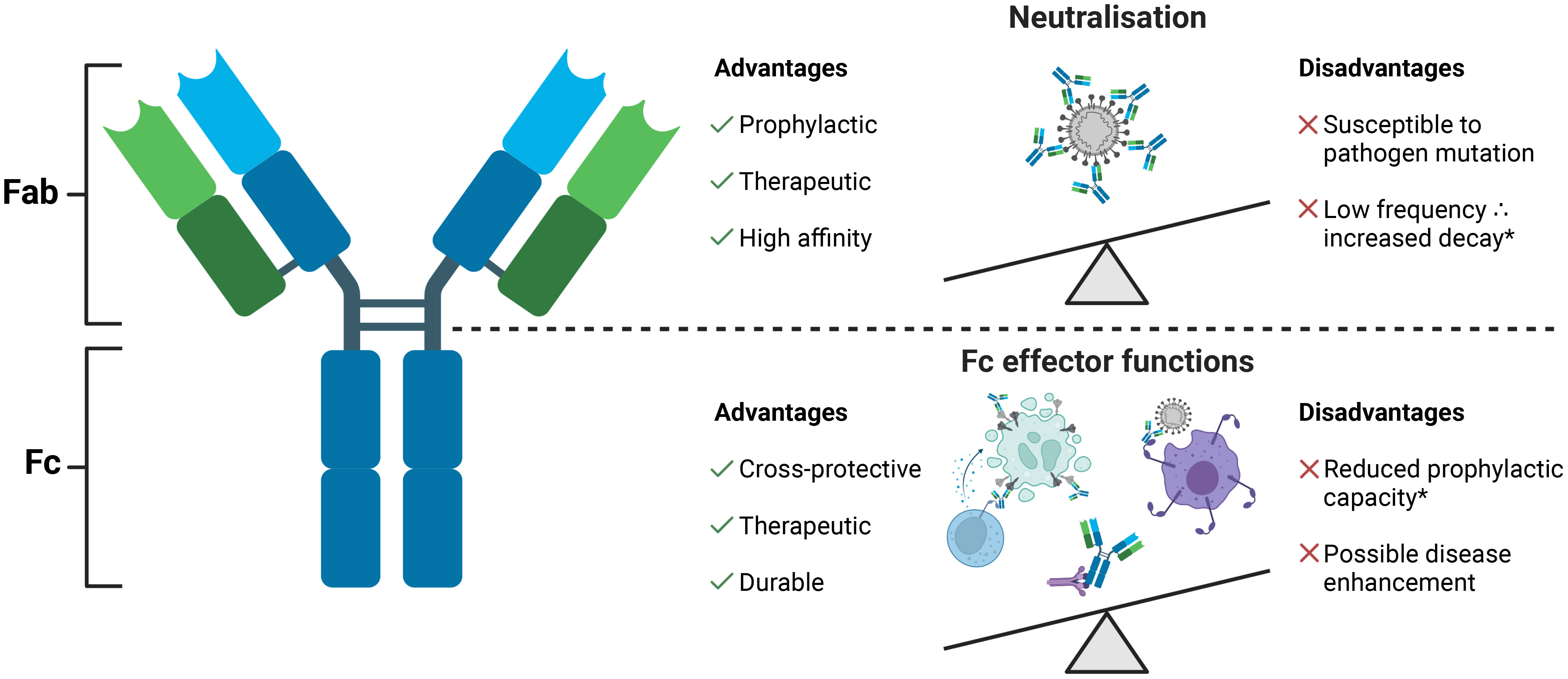
Frontiers Polyfunctional antibodies: a path towards precision vaccines for vulnerable populations
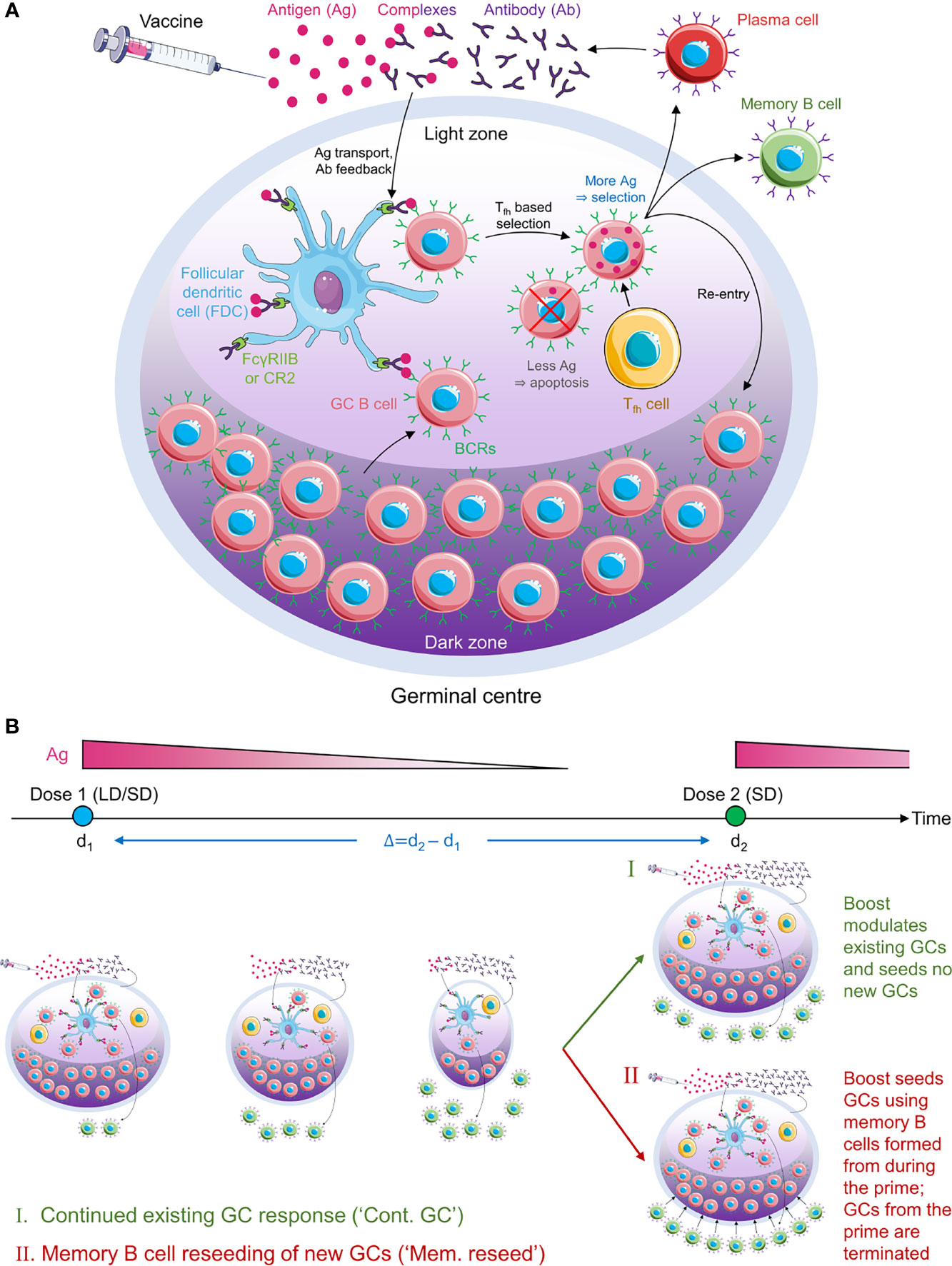
Frontiers Increased B Cell Selection Stringency In Germinal Centers Can Explain Improved COVID-19 Vaccine Efficacies With Low Dose Prime or Delayed Boost

Persistence of MERS-CoV-spike-specific B cells and antibodies after late third immunization with the MVA-MERS-S vaccine - ScienceDirect

Controlling timing and location in vaccines - ScienceDirect
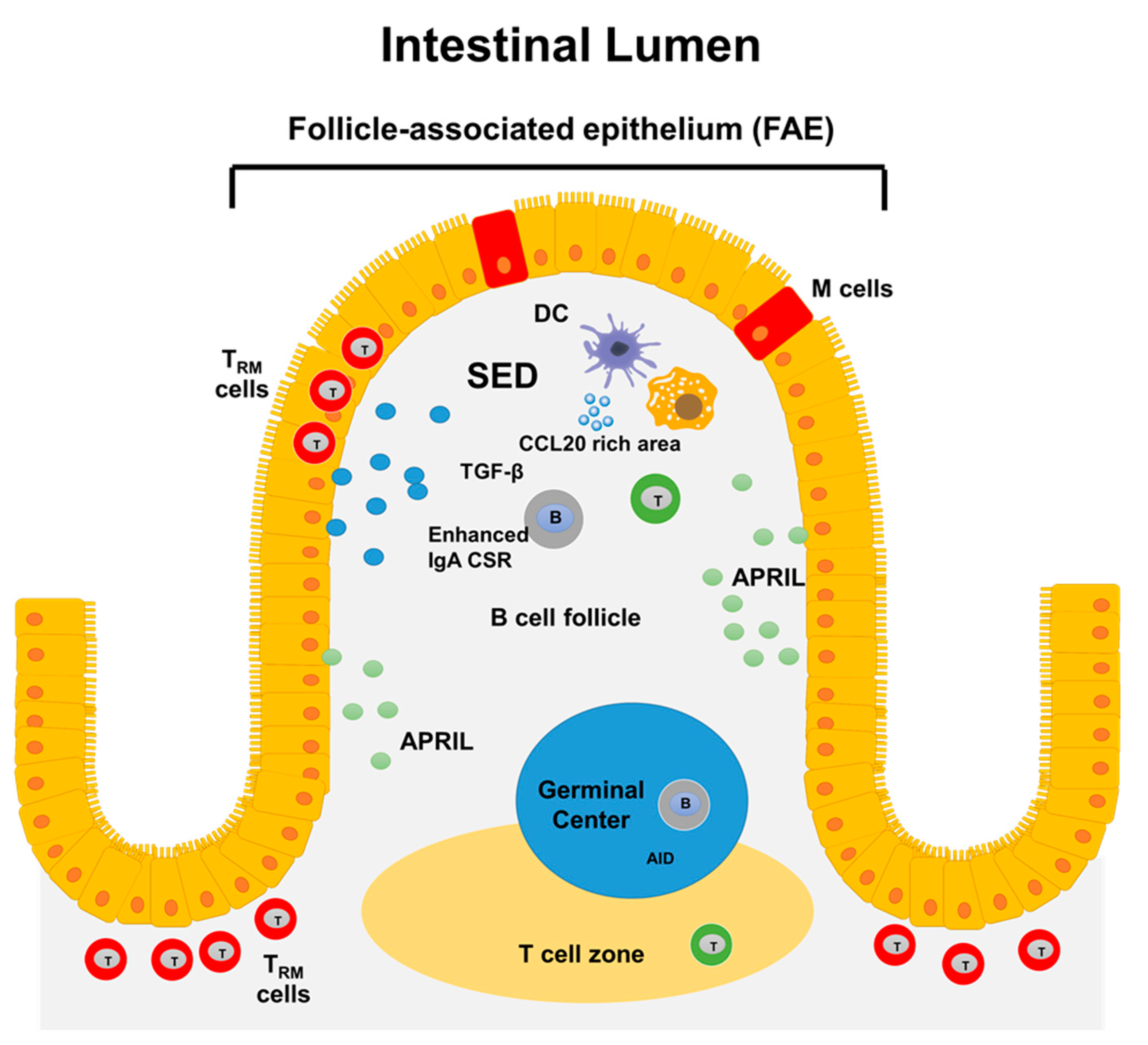
Vaccines, Free Full-Text

Antibodies from primary humoral responses modulate the recruitment of naive B cells during secondary responses - ScienceDirect

Persistence and post-antigen recall responses of HBsAg-specific

New insights into human immune memory from SARS‐CoV‐2 infection and vaccination - Hartley - 2022 - Allergy - Wiley Online Library

Immunology and Technology of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Vaccines

Profiling Germinal Center-like B Cell Responses to Conjugate Vaccines Using Synthetic Immune Organoids
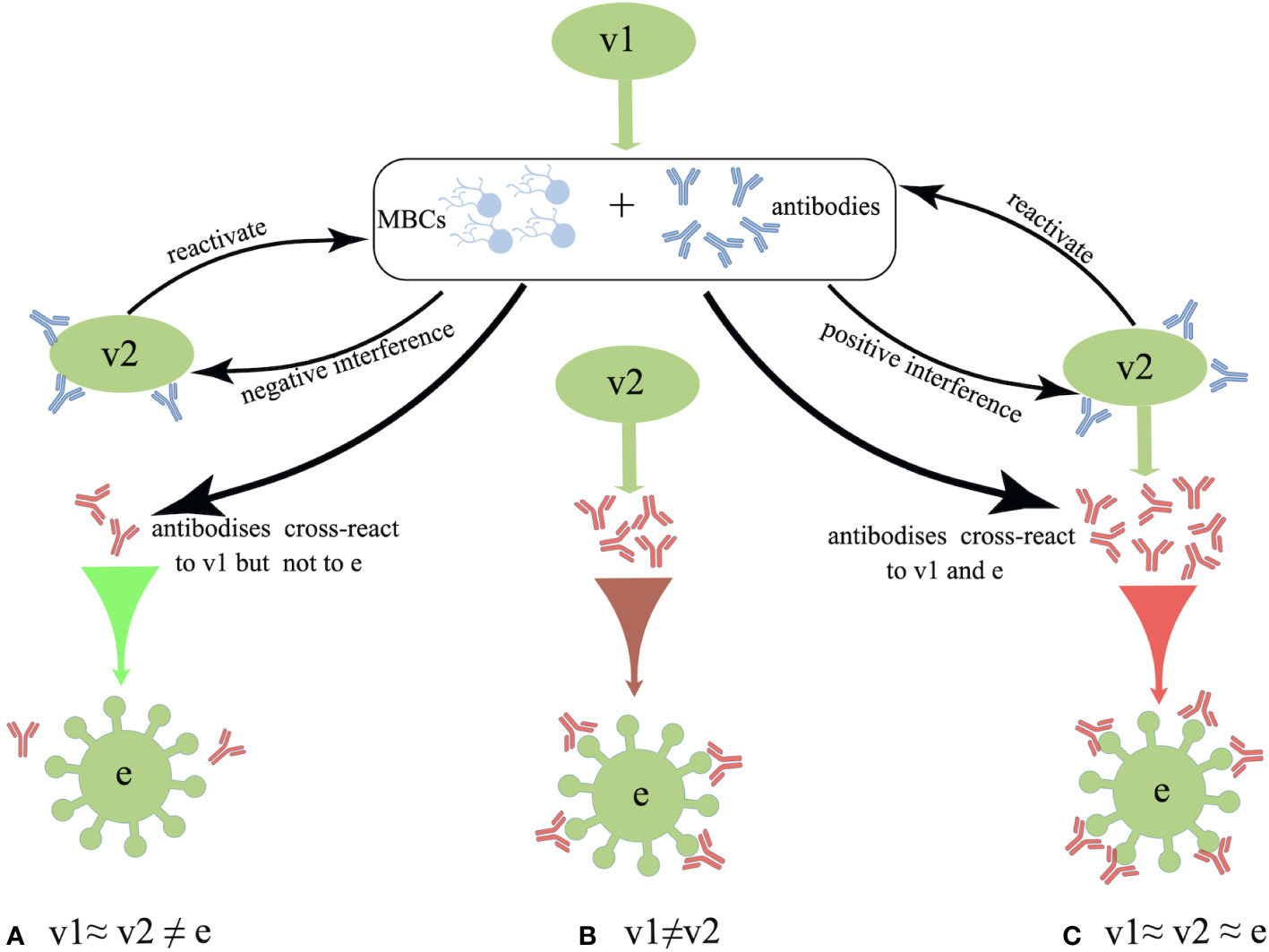
Frontiers Immune interference in effectiveness of influenza and COVID-19 vaccination

High-affinity memory B cells induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection produce more plasmablasts and atypical memory B cells than those primed by mRNA vaccines - ScienceDirect

Distinct antibody and memory B cell responses in SARS-CoV-2 naïve and recovered individuals after mRNA vaccination
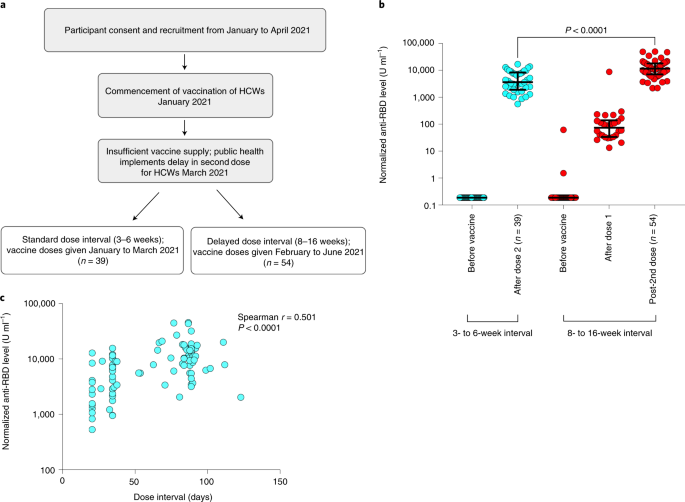
Delayed-interval BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccination enhances humoral immunity and induces robust T cell responses
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)