Metabolites, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
This research focused on establishing a hierarchy concerning the influence of various biological markers and body composition parameters on preventing, diagnosing and managing Metabolic Syndrome (MetS). Our cross-sectional cohort study included 104 subjects without any atherosclerotic antecedent pathology, organized in two groups (with and without MetS). All participants underwent clinical and anthropometric measurements, DEXA investigation and blood tests for all MetS criteria, together with adiponectin, leptin, insulin, uric acid and CRP. Based on mathematical logic, we calculated a normalized sensitivity score to compare the predictive power of biomarkers and parameters associated with MetS, upon the prevalence of MetS. Patients with MetS report higher levels of uric acid (p = 0.02), CRP (p = 0.012) and lower levels of adiponectin (p = 0.025) than patients without MetS. The top three biological markers with the highest predictive power of the prevalence of the disease are HDL, insulin, and adiponectin:leptin ratio, and the top three body composition parameters are trunk fat-free percentage, waist-height ratio and trunk fat percentage. Their high sensitivity scores differentiate them from all the other markers analysed in the study. Our findings report relevant scores for estimating the importance of cardiometabolic risks in the prevalence of MetS. The high rank of protective markers, HDL and trunk fat-free percentage, suggest that positive effects have a stronger association with the prevalence of MetS, than negative ones do. Therefore, this risk stratification study provides important support for prevention and management programs regarding MetS.
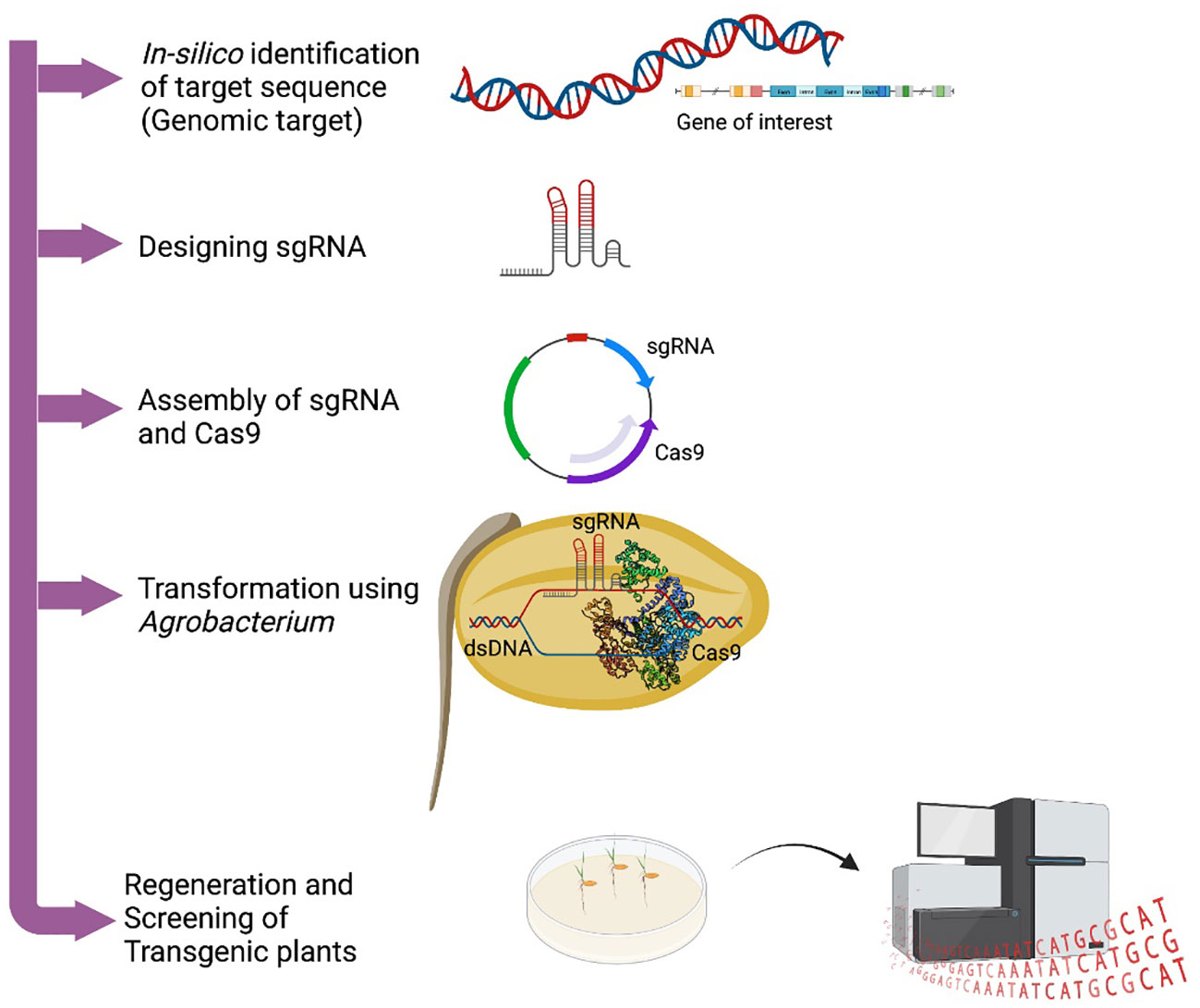
Frontiers Metabolic engineering of plant secondary metabolites: prospects and its technological challenges

Metabolism - Incomplete Oxidation, Energy Production, Enzymes

Codeine Intoxication Associated with Ultrarapid CYP2D6 Metabolism

The American Journal of Pathology

Exercise training enhances muscle mitochondrial metabolism in diet-resistant obesity - eBioMedicine
Phagocytes, toxic oxygen metabolites and inflammatory bowel disease: implications for treatment. - Abstract - Europe PMC
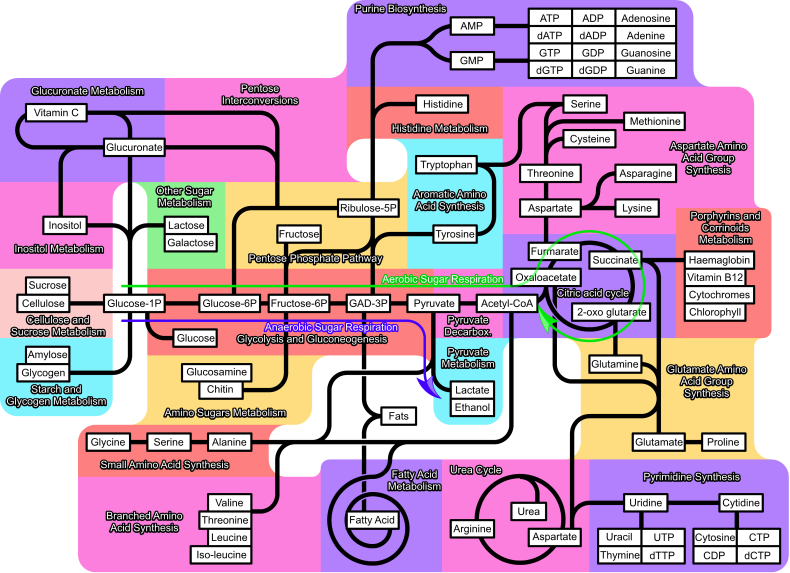
File:Metabolism 790px.png - Wikipedia

Time of day determines postexercise metabolism in mouse adipose tissue
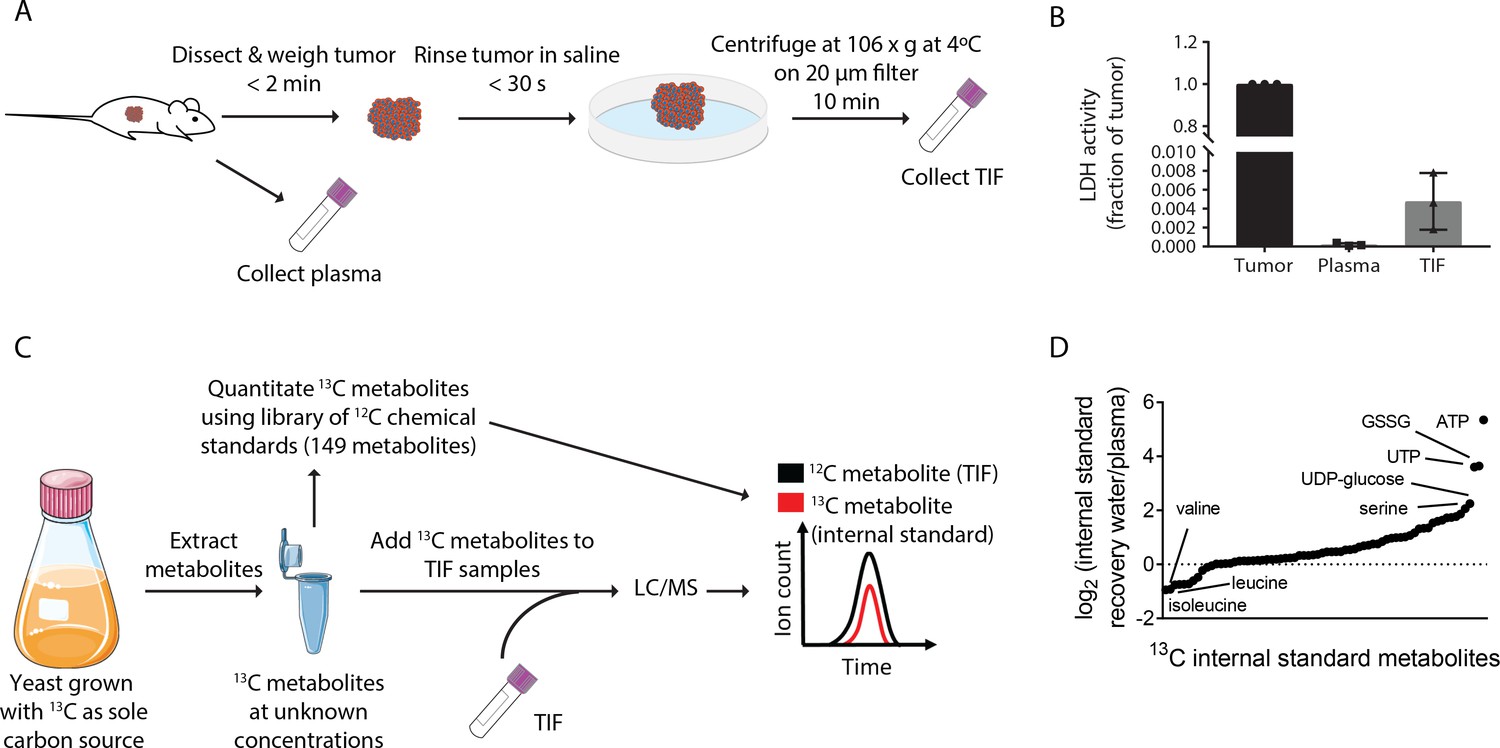
Quantification of microenvironmental metabolites in murine cancers reveals determinants of tumor nutrient availability
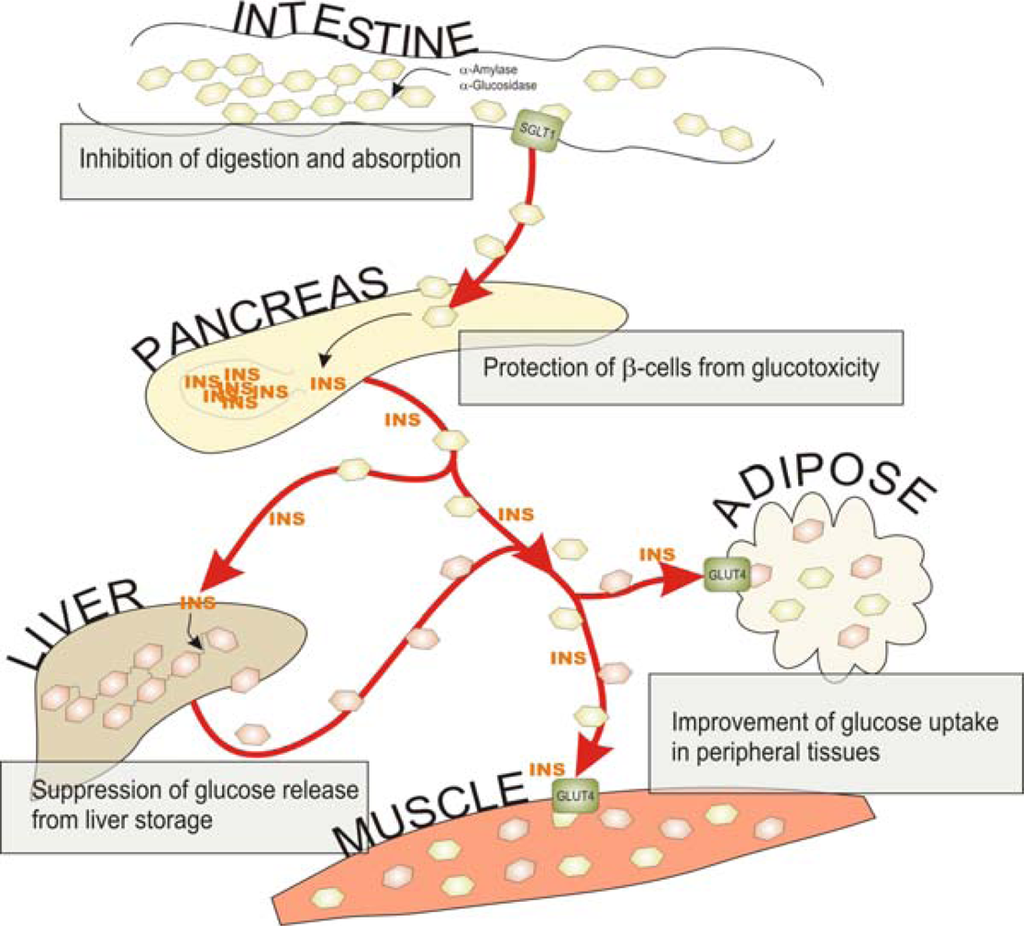
IJMS, Free Full-Text
Agonistic effect of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) and its metabolites on brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) through molecular docking simulation. : Vetrivel, Umashankar : Free Download, Borrow, and Streaming : Internet Archive

Identification of Metabolite Interference Is Necessary for Accurate LC-MS Targeted Metabolomics Analysis

Tmq C-Plot Get File - Colaboratory

Ketoconazole beyond antifungal activity: Bioinformatics‐based hypothesis on lipid metabolism in dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis - Goularte‐Silva - 2022 - Experimental Dermatology - Wiley Online Library
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)