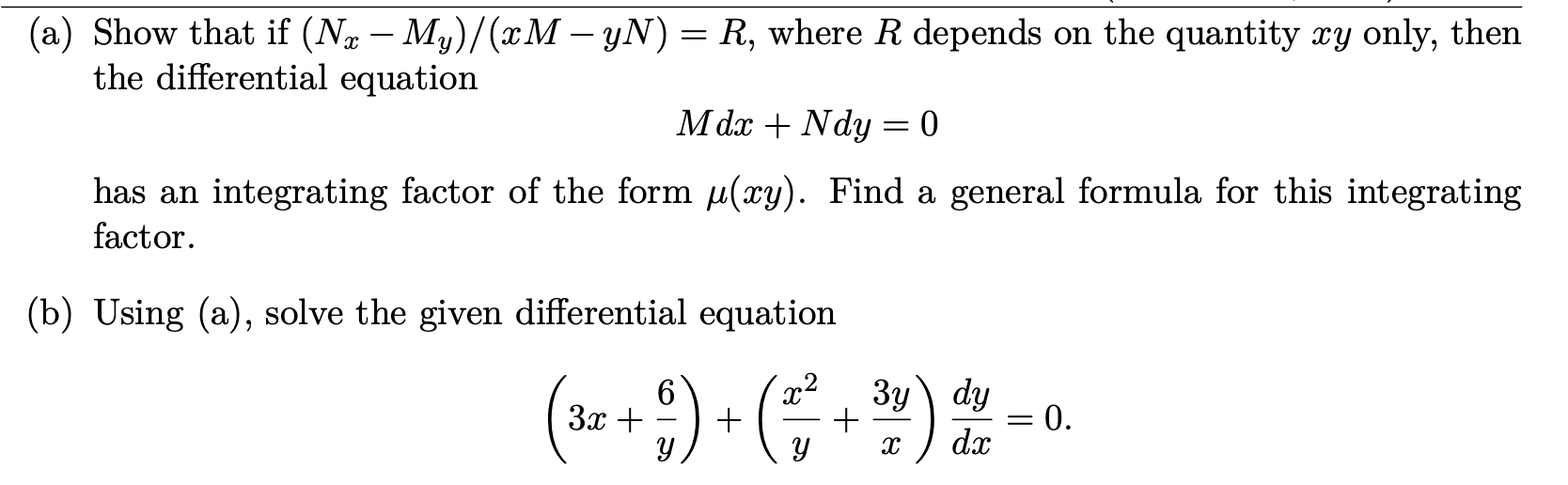
Show that if (Nx−My)/(xM−yN)=R, where R depends on the quant
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição

SOLVED: Nx - My = R, where R is a function depending only on the quantity z = XY, then the differential equation xM - YN + Ny = 0 has an

Nurul A. Chowdhury - Numerical Methods, PDF, Numerical Analysis

Optimization of Complex Systems: Theory, Models, Algorithms and Applications, PDF, Mathematical Optimization

Solved If N - M, XM – YN = R, where R is a function

Transcendental Number Theory - Stanford University

A(H3C3N3O3)(NO3) (A = K, Rb): Alkali-Metal Nitrate Isocyanurates with Strong Optical Anisotropy

Full article: Oxides, Oxides, and More Oxides: High-κ Oxides, Ferroelectrics, Ferromagnetics, and Multiferroics

Conduction Heat Transfer Notes for MECH 7210 - Auburn University

Problems in general physics by Mateus Pereira - Issuu
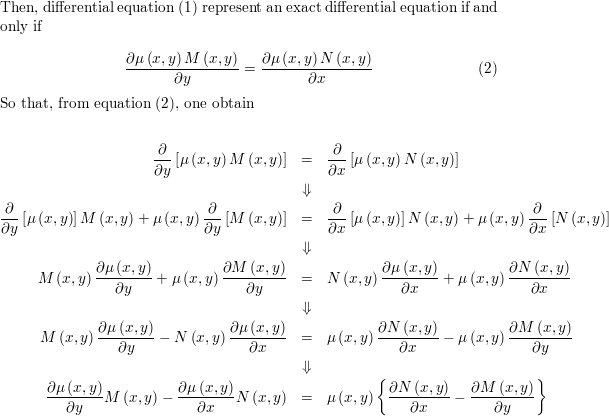
Show that if (Nx−My)/(xM−yN)=R, where R depends on the quant

Differential Equations - users-deprecated.aims.ac.za

Solved - M y -R, where R is a function depending only on the

Mathematical Methods for Physics and Engineering - Matematica.NET
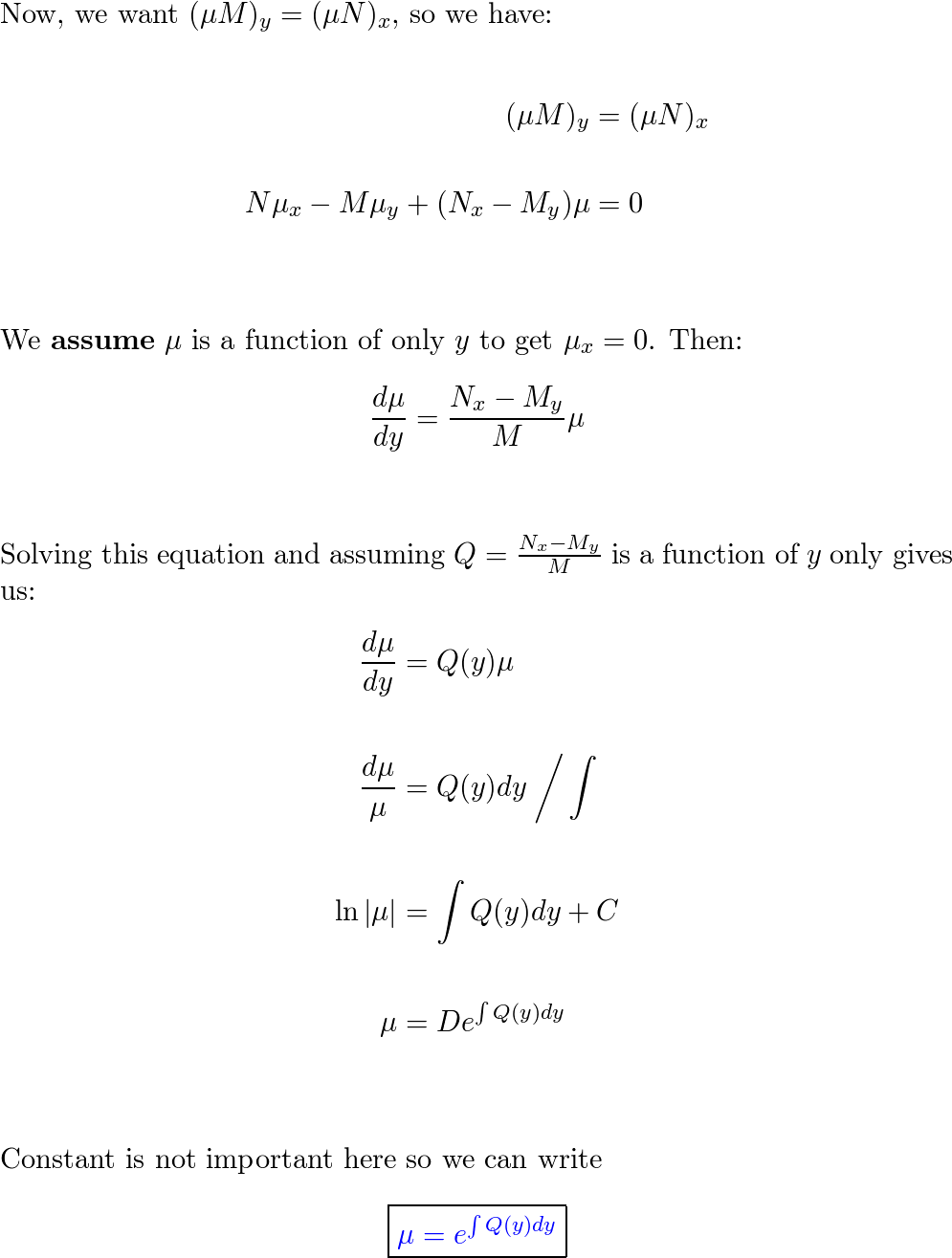
Show that if (Nx − My)/M = Q, where Q is a function of y onl

Dicopper(I) Sites Confined in a Single Metal–Organic Layer Boosting the Electroreduction of CO2 to CH4 in a Neutral Electrolyte
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)