Oxidative Stress: A Pathogenic Mechanism for Niemann-Pick Type C
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
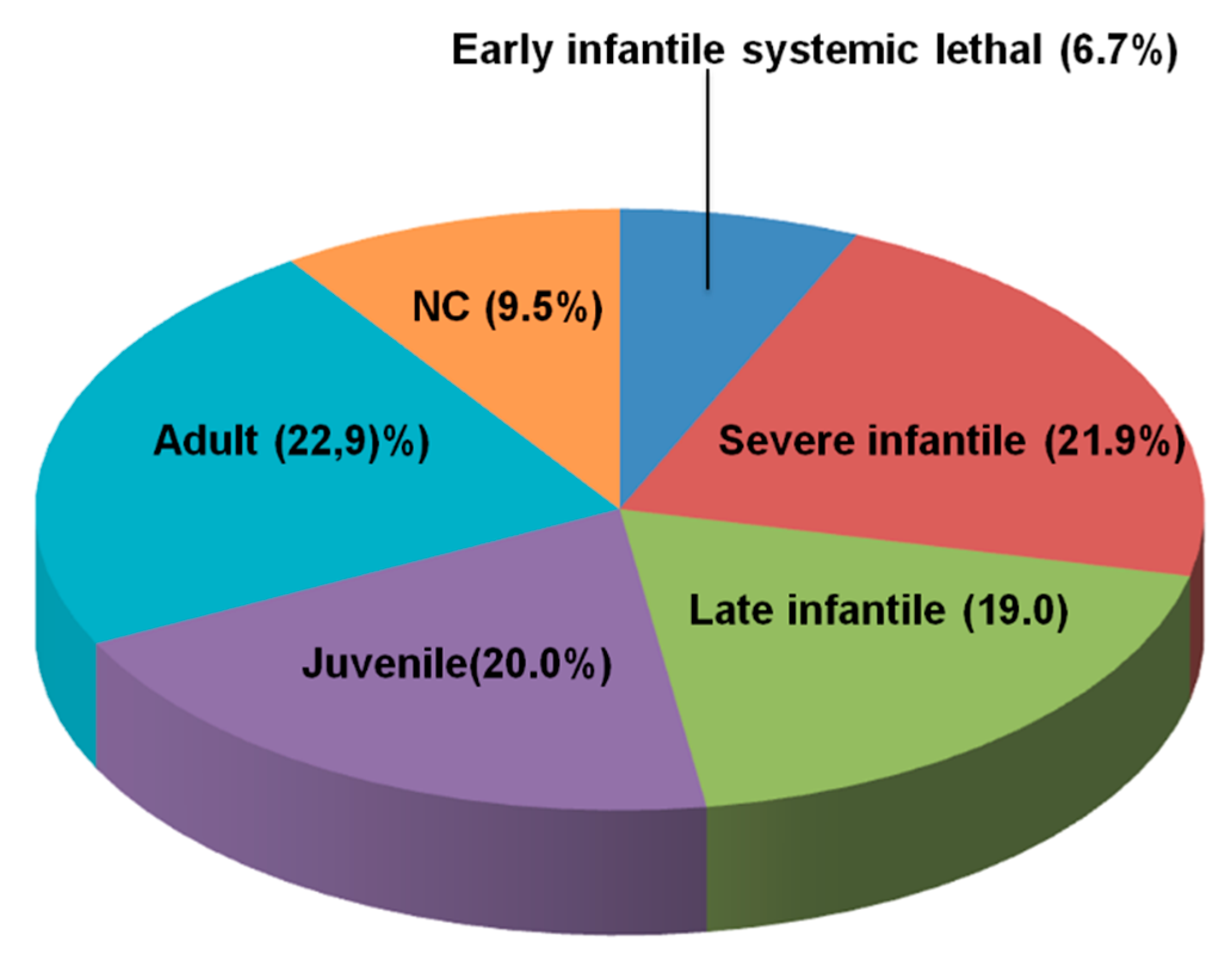
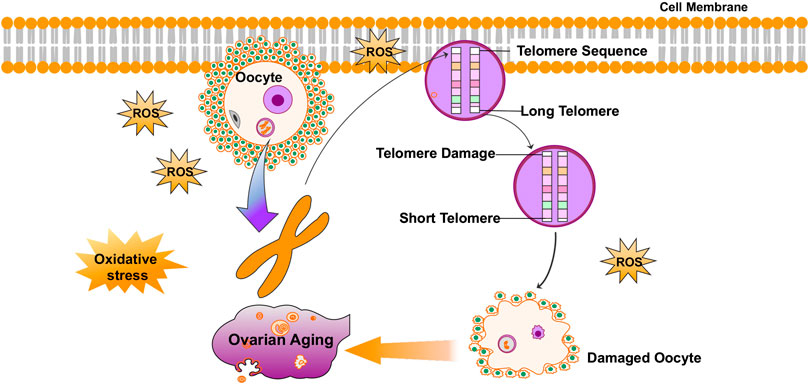
Niemann-Pick type C (NPC) disease is a neurovisceral atypical lipid storage disorder involving the accumulation of cholesterol and other lipids in the late endocytic pathway. The pathogenic mechanism that links the accumulation of intracellular cholesterol with cell death in NPC disease in both the CNS and the liver is currently unknown. Oxidative stress has been observed in the livers and brains of NPC mice and in different NPC cellular models. Moreover, there is evidence of an elevation of oxidative stress markers in the serumof NPC patients. Recent evidence strongly suggests that mitochondrial dysfunction plays an important role in NPC pathogenesis and that mitochondria could be a significant source of oxidative stress in this disease. In this context, the accumulation of vitamin E in the late endosomal/lysosomal compartments in NPC could lead to a potential decrease of its bioavailability and could be another possible cause of oxidative damage. Another possible source of reactive species in NPC is the diminished activity of different antioxidant enzymes. Moreover, because NPC is mainly caused by the accumulation of free cholesterol, oxidized cholesterol derivatives produced by oxidative stress may contribute to the pathogenesis of the disease.
Frontiers The Role of Oxidative Stress and Natural Antioxidants

Neuronal gene repression in Niemann–Pick type C models is mediated

Identification of Niemann-Pick C1 disease biomarkers through

Evidence of redox imbalance and mitochondrial dysfunction in
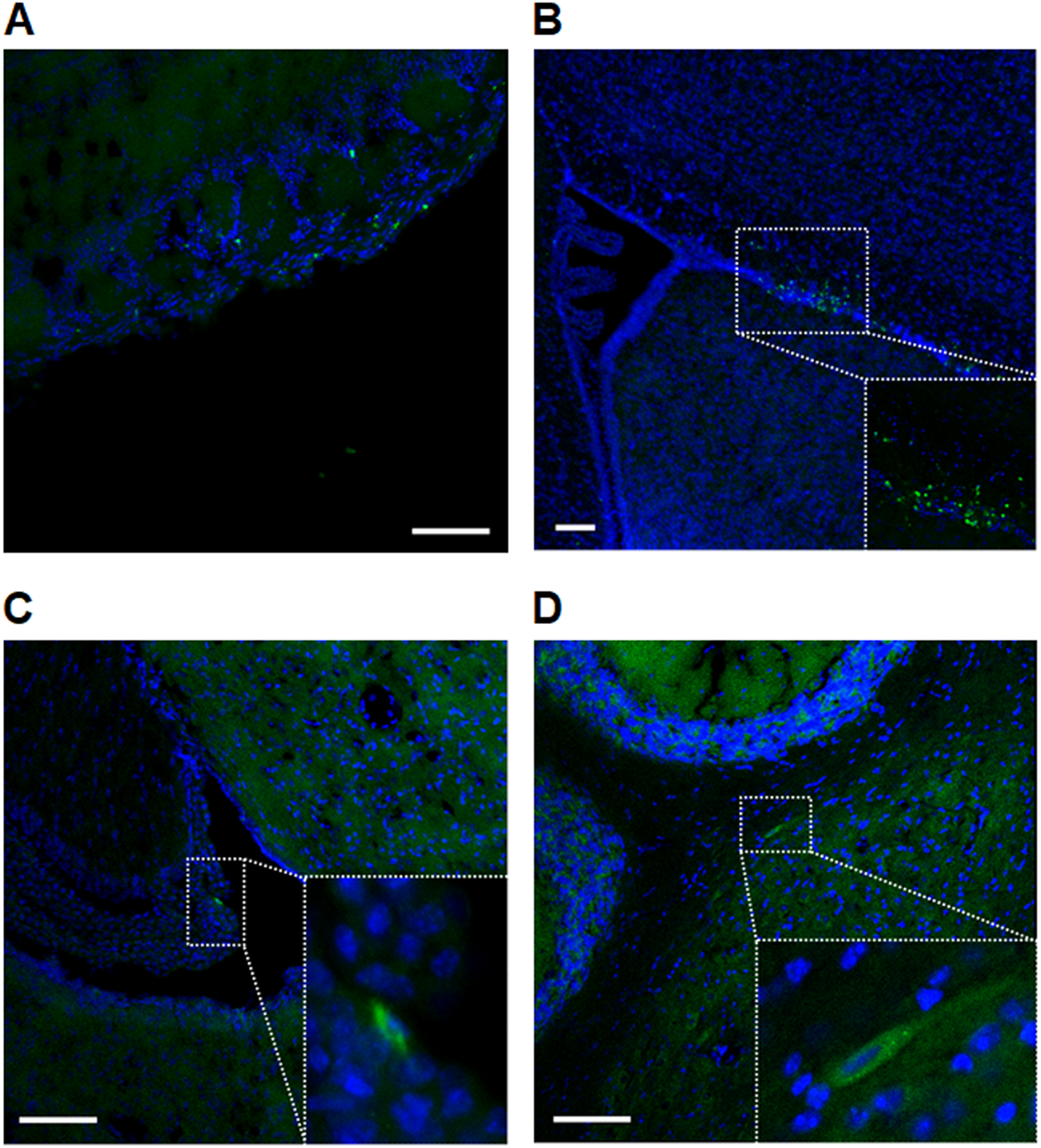
Stem cell-secreted 14,15- epoxyeicosatrienoic acid rescues

Imaging of neuroinflammation in adult Niemann-Pick type C disease
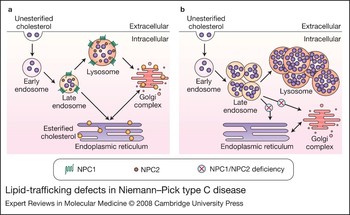
The pathogenesis of Niemann–Pick type C disease: a role for

The role of oxidative stress in the development and
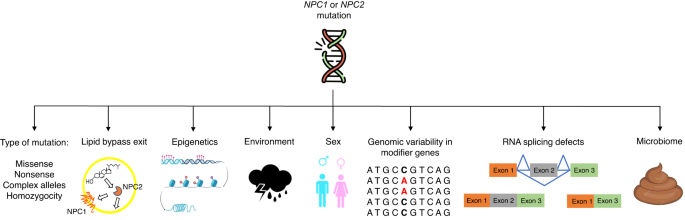
Understanding the phenotypic variability in Niemann-Pick disease
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)