Biofilm-Associated Agr and Sar Quorum Sensing Systems of Staphylococcus aureus Are Inhibited by 3-Hydroxybenzoic Acid Derived from Illicium verum
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição

Structural and function analyses of the global regulatory protein SarA from Staphylococcus aureus. - Abstract - Europe PMC
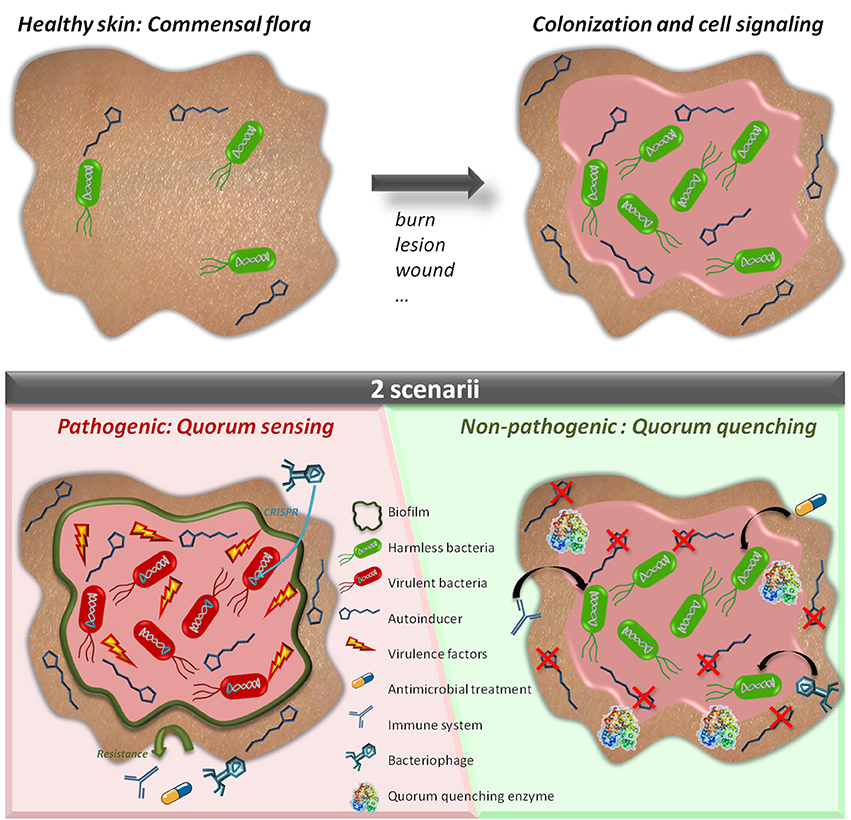
Frontiers Interference in Bacterial Quorum Sensing: A Biopharmaceutical Perspective

Octanoic acid promotes clearance of antibiotic-tolerant cells and eradicates biofilms of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from recurrent bovine mastitis - ScienceDirect

Staphylococcal Biofilms: Pathogenicity, Mechanism and Regulation of Biofilm Formation by Quorum-Sensing System and Antibiotic Resistance Mechanisms of Biofilm-Embedded Microorganisms

Squalenyl Hydrogen Sulfate Nanoparticles for Simultaneous Delivery of Tobramycin and an Alkylquinolone Quorum Sensing Inhibitor Enable the Eradication of P. aeruginosa Biofilm Infections - Ho - 2020 - Angewandte Chemie International Edition - Wiley

Octanoic acid promotes clearance of antibiotic-tolerant cells and eradicates biofilms of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from recurrent bovine mastitis - ScienceDirect
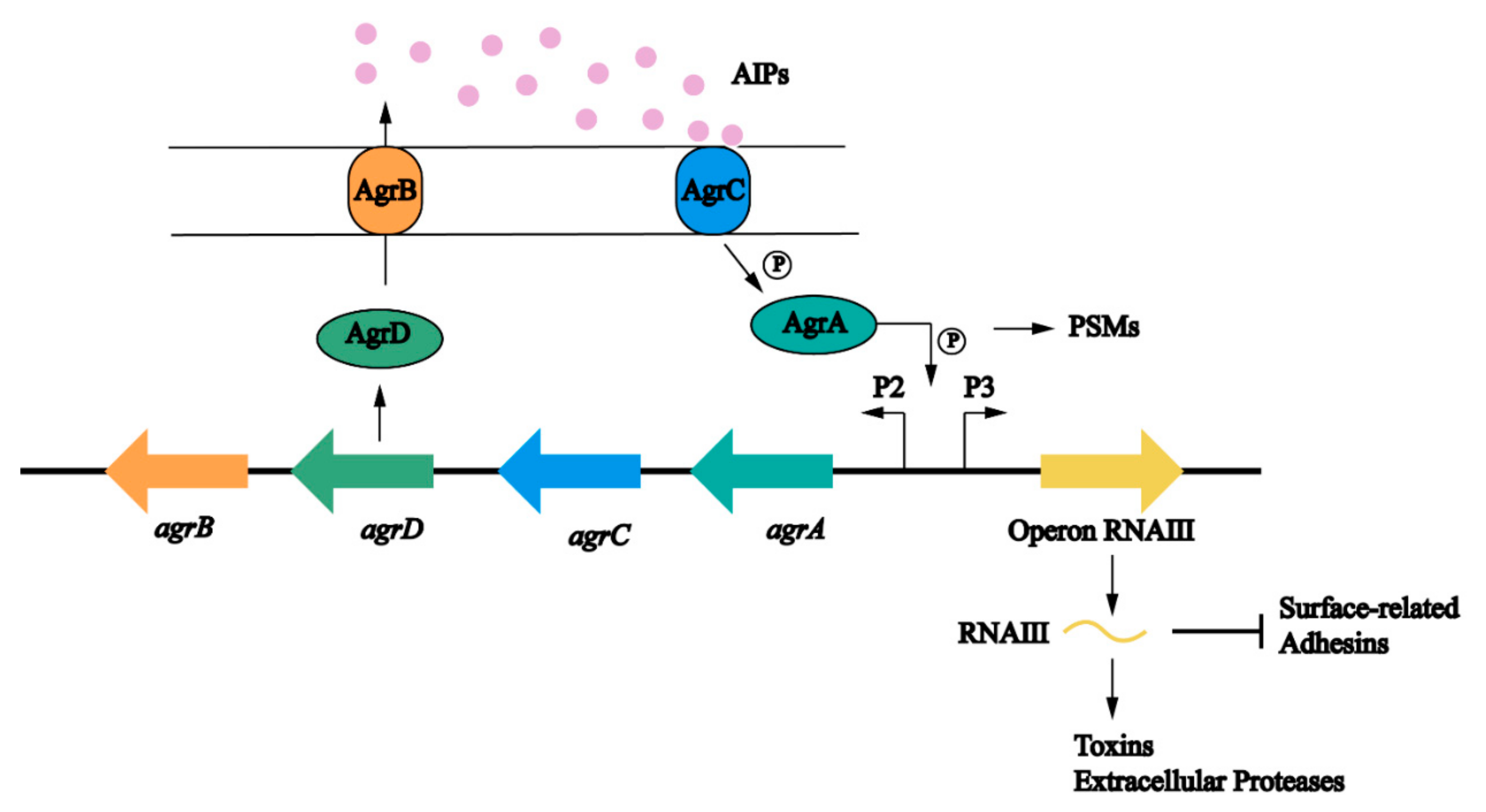
Antibiotics, Free Full-Text

Biofilm-Associated Agr and Sar Quorum Sensing Systems of Staphylococcus aureus Are Inhibited by 3-Hydroxybenzoic Acid Derived from Illicium verum. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Comparative evaluation of small molecules reported to be inhibitors of Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation

Biofilm-Associated Agr and Sar Quorum Sensing Systems of Staphylococcus aureus Are Inhibited by 3-Hydroxybenzoic Acid Derived from Illicium verum

Computational tools for exploring peptide-membrane interactions in gram-positive bacteria - ScienceDirect
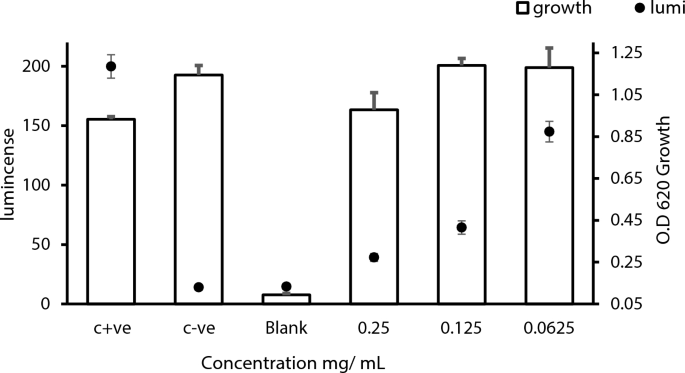
Ziziphus spina-christi (L.) Willd. Leaves Extract Affecting agr Quorum Sensing System in Staphylococcus aureus

Staphylococcal Biofilms: Pathogenicity, Mechanism and Regulation of Biofilm Formation by Quorum-Sensing System and Antibiotic Resistance Mechanisms of Biofilm-Embedded Microorganisms

Quorum-sensing agr system of Staphylococcus aureus primes gene expression for protection from lethal oxidative stress
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/staph-infections-3156887-FINAL2-48c3a7caea8f429a94f7d074e66d5842.png)