The diversity and commonalities of the radiation-resistance
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
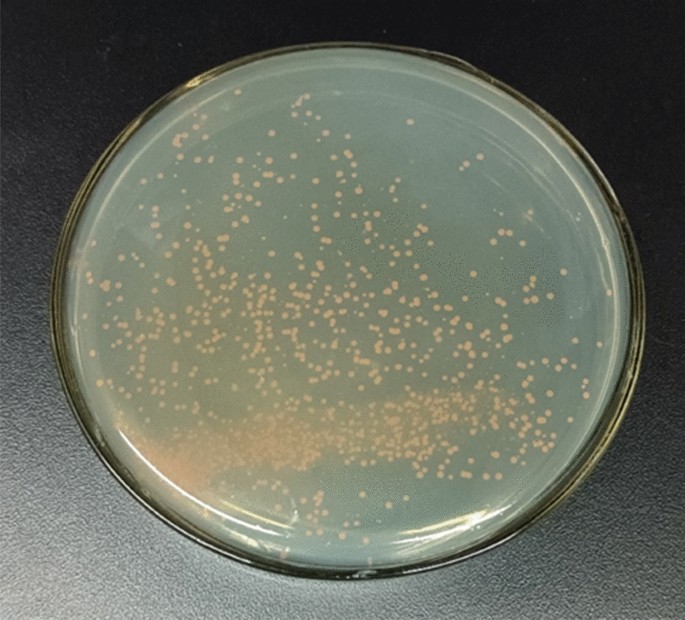
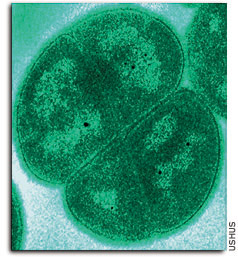
Deinococcus is an extremophilic microorganism found in a wide range of habitats, including hot springs, radiation-contaminated areas, Antarctic soils, deserts, etc., and shows some of the highest levels of resistance to ionizing radiation known in nature. The highly efficient radiation-protection mechanisms of Deinococcus depend on a combination of passive and active defense mechanisms, including self-repair of DNA damage (homologous recombination, MMR, ER and ESDSA), efficient cellular damage clearance mechanisms (hydrolysis of damaged proteins, overexpression of repair proteins, etc.), and effective clearance of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Due to these mechanisms, Deinococcus cells are highly resistant to oxidation, radiation and desiccation, which makes them potential chassis cells for wide applications in many fields. This article summarizes the latest research on the radiation-resistance mechanisms of Deinococcus and prospects its biotechnological application potentials.

Antibiotics, Free Full-Text
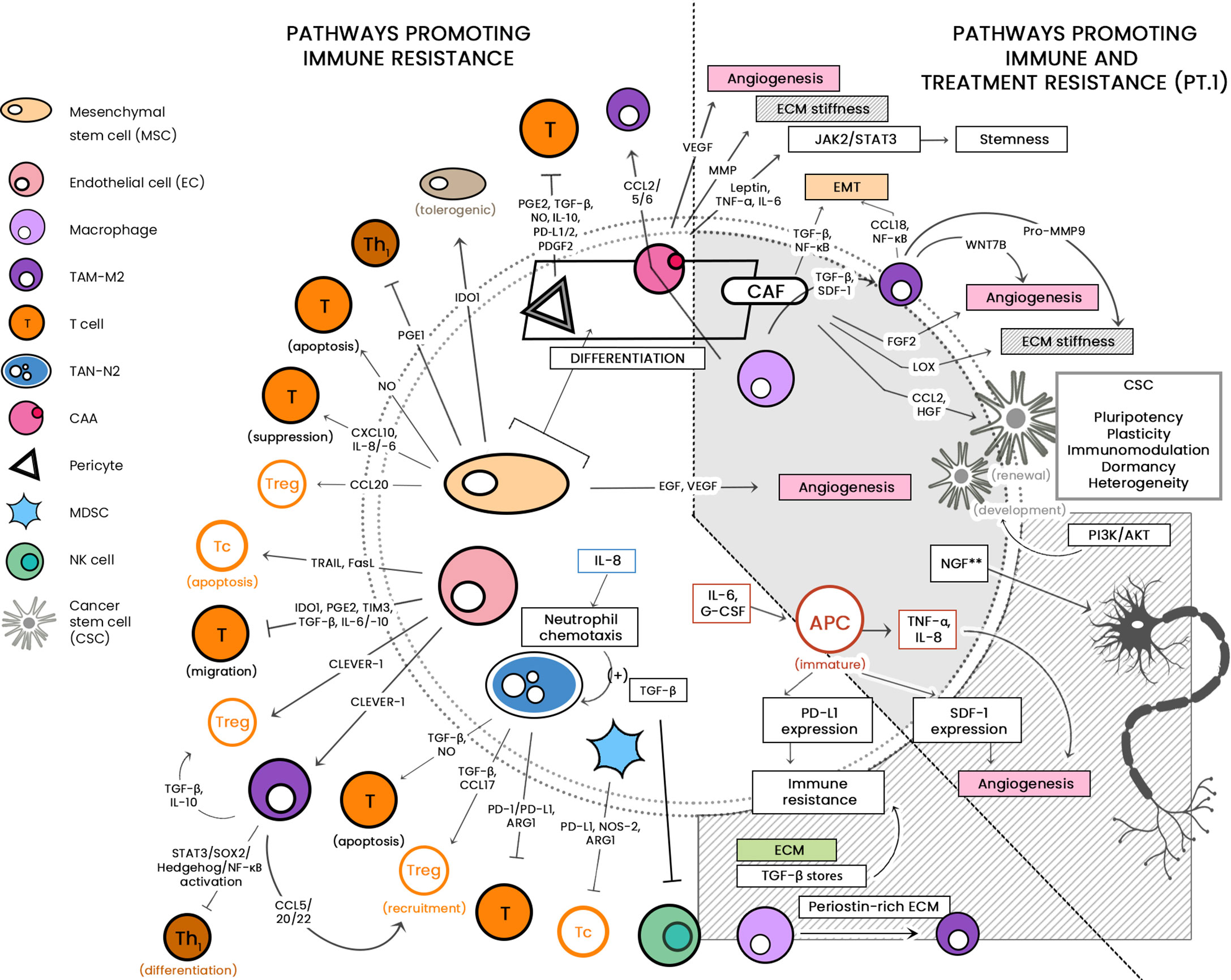
Frontiers Aspects of the Tumor Microenvironment Involved in Immune Resistance and Drug Resistance

Epigenetics - Wikipedia

Tumor microenvironment and radioresistance
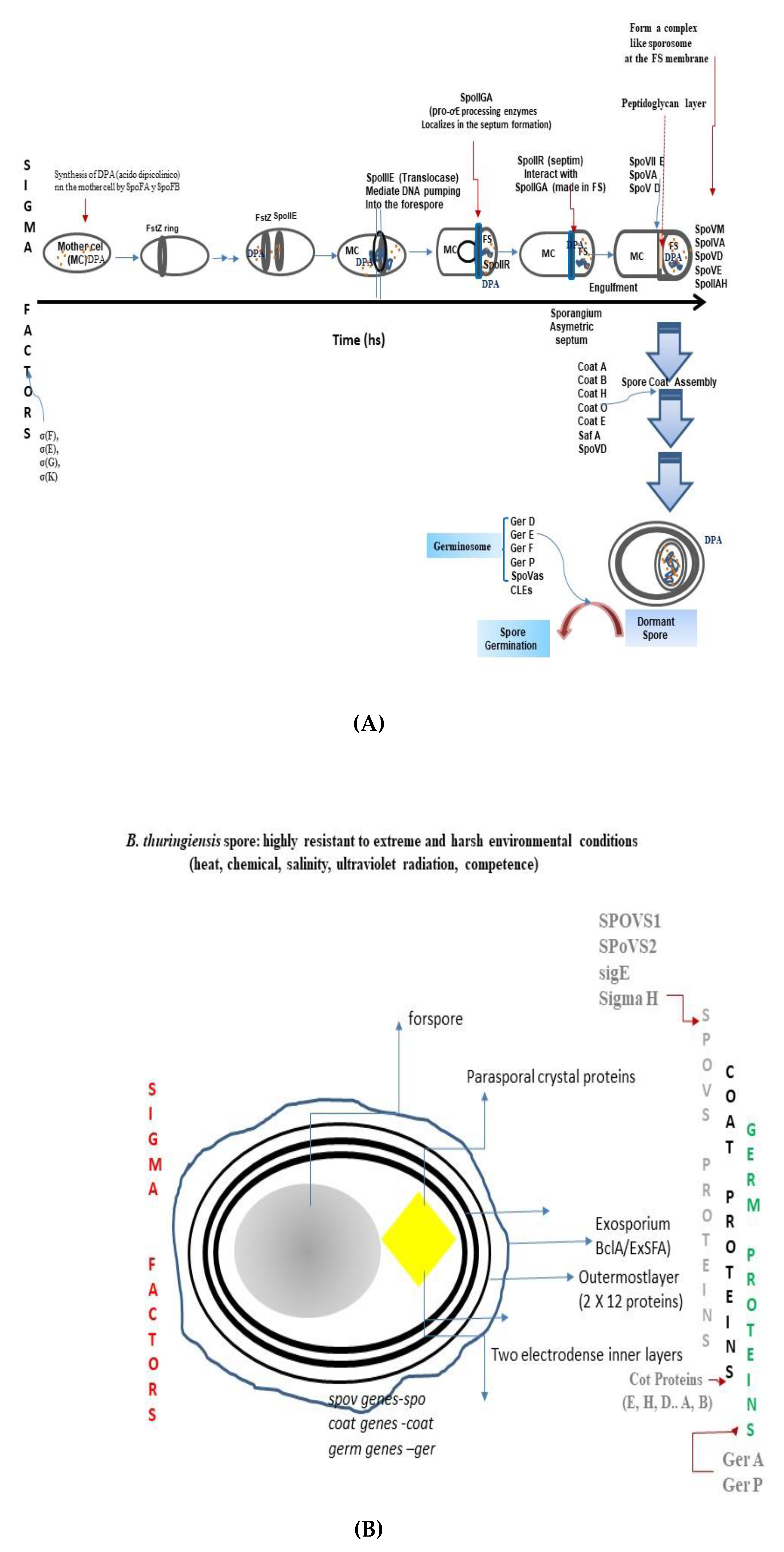
Microbiology Research, Free Full-Text
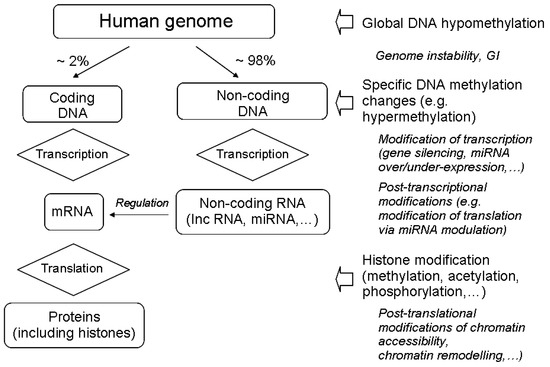
IJMS, Free Full-Text
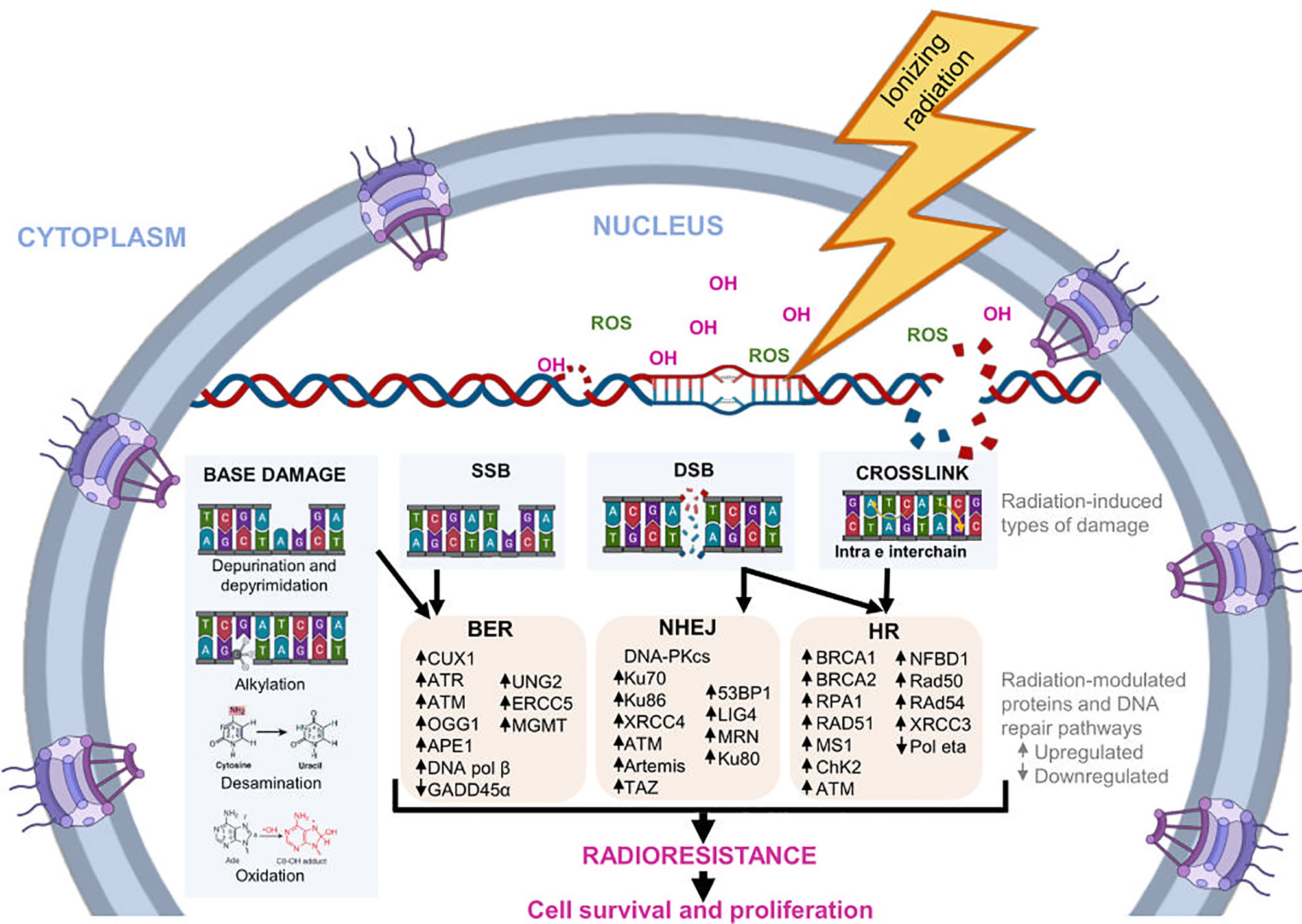
Frontiers Biological Adaptations of Tumor Cells to Radiation Therapy

Microorganisms, Free Full-Text
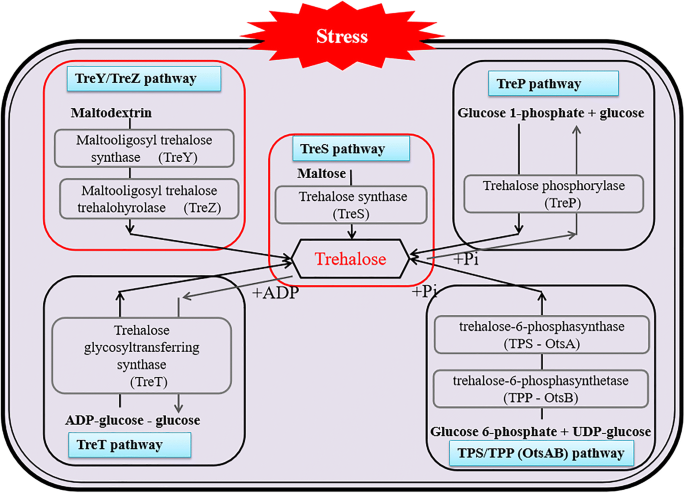
The diversity and commonalities of the radiation-resistance mechanisms of Deinococcus and its up-to-date applications, AMB Express

Radiation Resistance: Resurrection by Recombination - ScienceDirect
Diversity, Free Full-Text
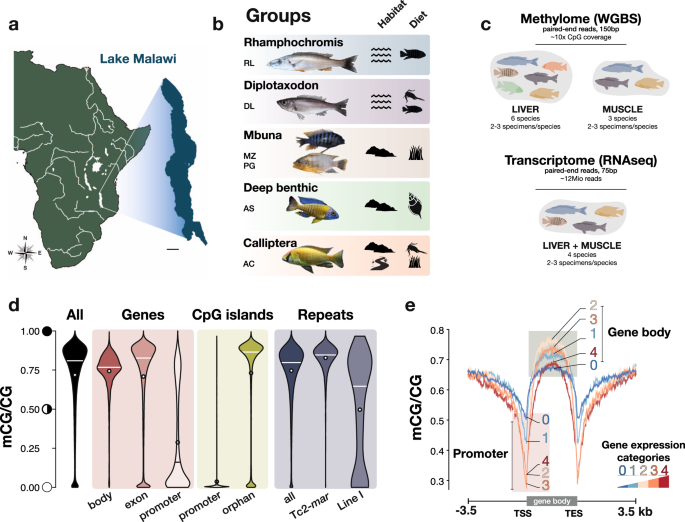
Mapping epigenetic divergence in the massive radiation of Lake Malawi cichlid fishes
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)