Analysis suggests child bullies have higher risk for substance use later in life
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Children and adolescents who bully their peers have a higher risk for drug, alcohol and tobacco use later in life, according to the results of a meta-analysis published in Pediatrics. Charlotte Vrijen, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Groningen in the Netherlands, and colleagues reviewed existing evidence regarding the association between peer bullying perpetration in

Substance use during the pandemic

Bullying - ACAMH
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-11515389521-ddde642afc5b41e597f4fb03bc8ddc97.jpg)
Bullying: What It Is, Types, and More

Cyberbullying and Children and Young People's Mental Health: A Systematic Map of Systematic Reviews
Bullying and the Brain

Behind the numbers: ending school violence and bullying
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-are-the-effects-of-cyberbullying-460558_color1-5b50c42946e0fb0037b84d00.png)
What Are the Effects of Cyberbullying on Children?
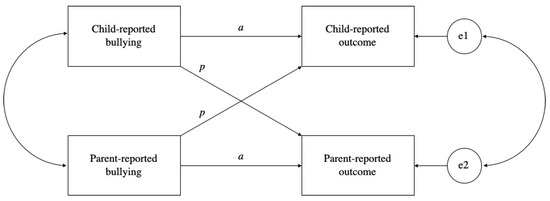
Children, Free Full-Text

Deal with a Bully and Overcome Bullying

Substance use, abuse, and addiction
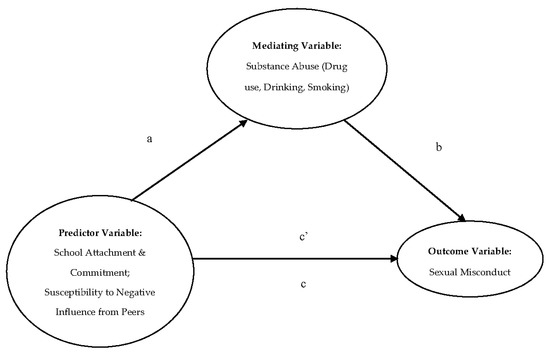
IJERPH, Free Full-Text

Childhood and Adolescent Bullying Perpetration and Later Substance Use: A Meta-analysis, Pediatrics
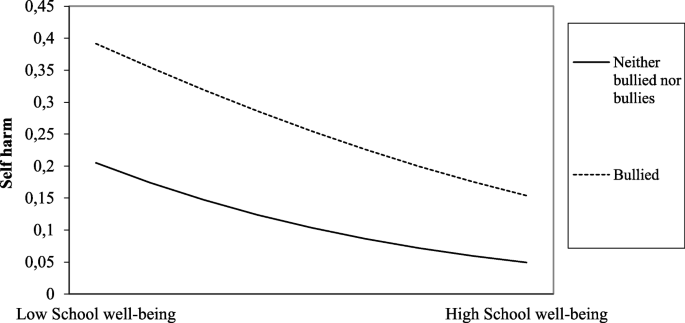
The relationship between self-harm and bullying behaviour: results from a population based study of adolescents, BMC Public Health

The Effects of Bullying on Mental Health - Best Day Psychiatry & Counseling
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)



.png)



