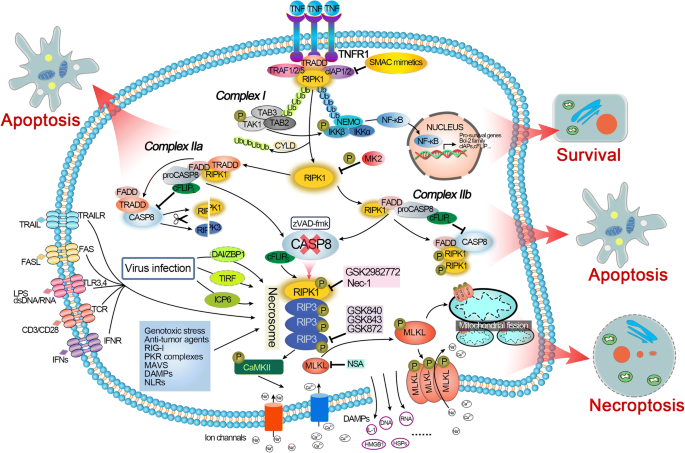
RVA-induced necrosome formation consisting of RIPK1, RIPK3, and MLKL
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição

Post-translational control of RIPK3 and MLKL
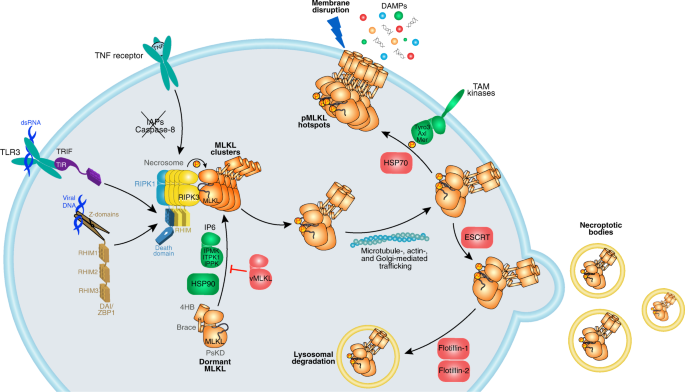
The regulation of necroptosis by post-translational modifications

RIPK3-and MLKL-dependent necroptosis mediated by various stimuli.

Targeting Necroptosis as a Promising Therapy for Alzheimer's Disease
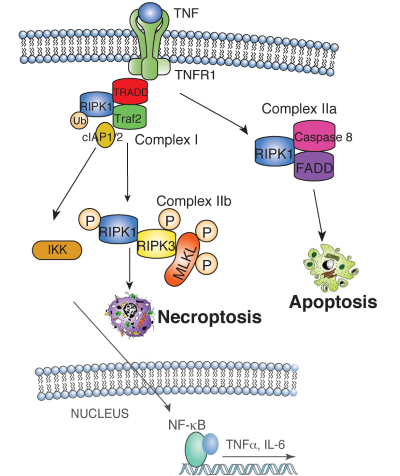
RIPK proteins in cell death and tissue homeostasis.

Necroptosis: a regulated inflammatory mode of cell death, Journal of Neuroinflammation

The Structural Basis of Necroptotic Cell Death Signaling: Trends in Biochemical Sciences
Bypassing drug resistance by triggering necroptosis: recent advances in mechanisms and its therapeutic exploitation in leukemia, Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research
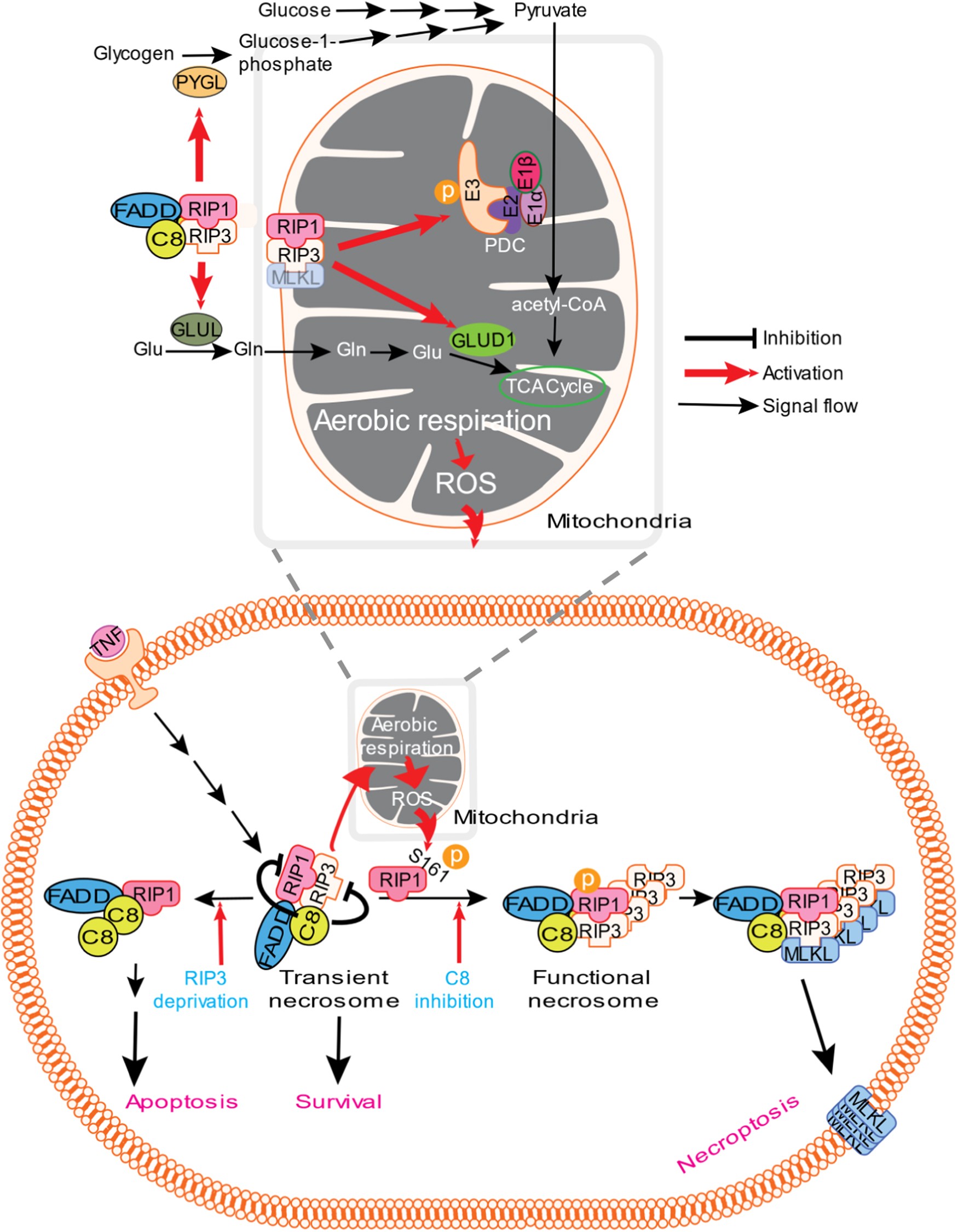
RIP3 is an upregulator of aerobic metabolism and the enhanced respiration by necrosomal RIP3 feeds back on necrosome to promote necroptosis
Shikonin overcomes drug resistance and induces necroptosis by regulating the miR-92a-1-5p/MLKL axis in chronic myeloid leukemia
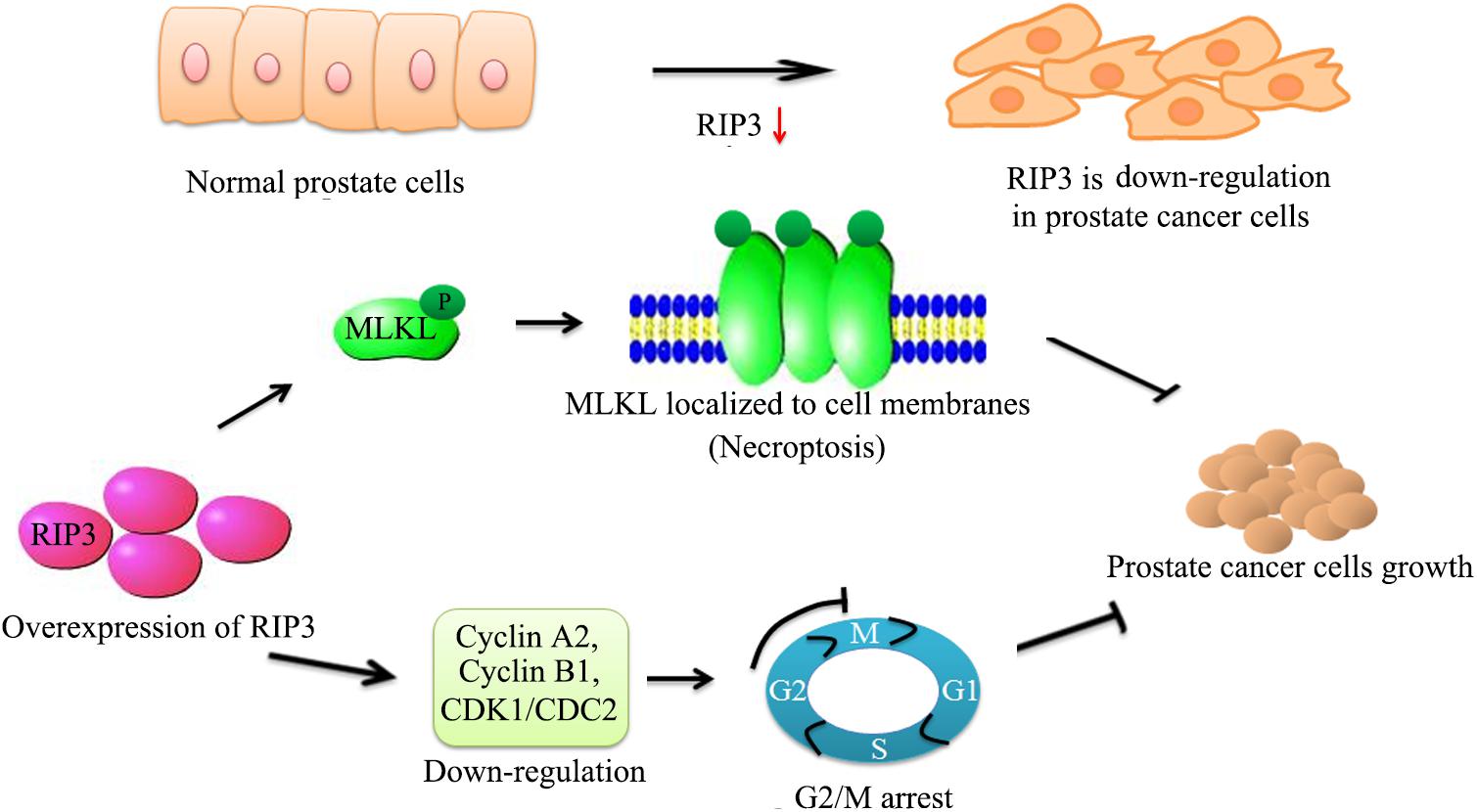
Frontiers Up-Regulation of RIP3 Alleviates Prostate Cancer Progression by Activation of RIP3/MLKL Signaling Pathway and Induction of Necroptosis

Apolipoprotein A1 Protects Against Necrotic Core Development in Atherosclerotic Plaques: PDZK1-Dependent High-Density Lipoprotein Suppression of Necroptosis in Macrophages
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)