Fiber deprivation and microbiome-borne curli shift gut bacterial populations and accelerate disease in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease - ScienceDirect
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurological disorder characterized by motor dysfunction, dopaminergic neuron loss, and alpha-synuclein (αSyn) inclusion…
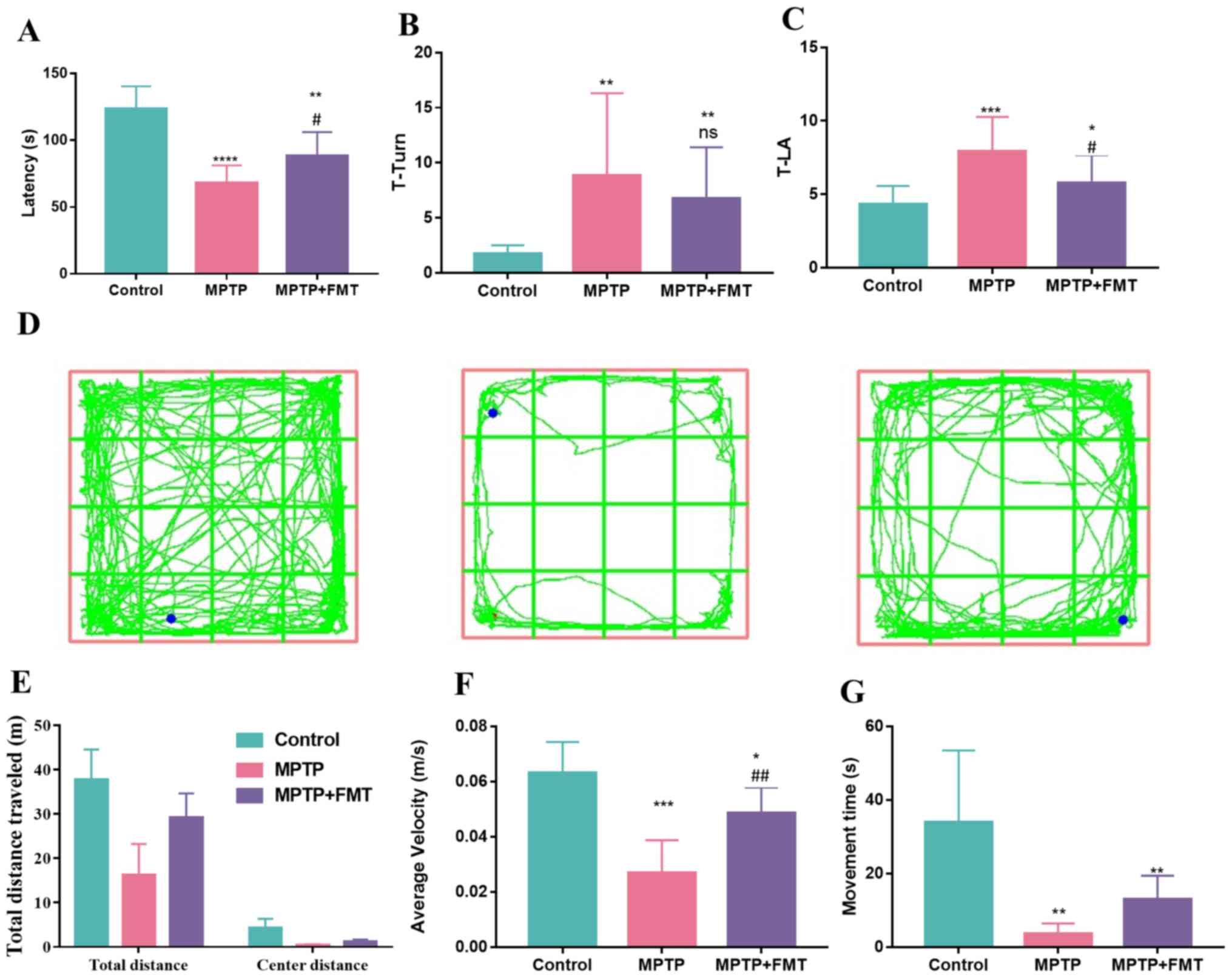
Gut microbiota relieves inflammation in the substantia nigra of chronic Parkinson's disease by protecting the function of dopamine neurons

Gut Microbiota Regulate Motor Deficits and Neuroinflammation in a Model of Parkinson's Disease - ScienceDirect
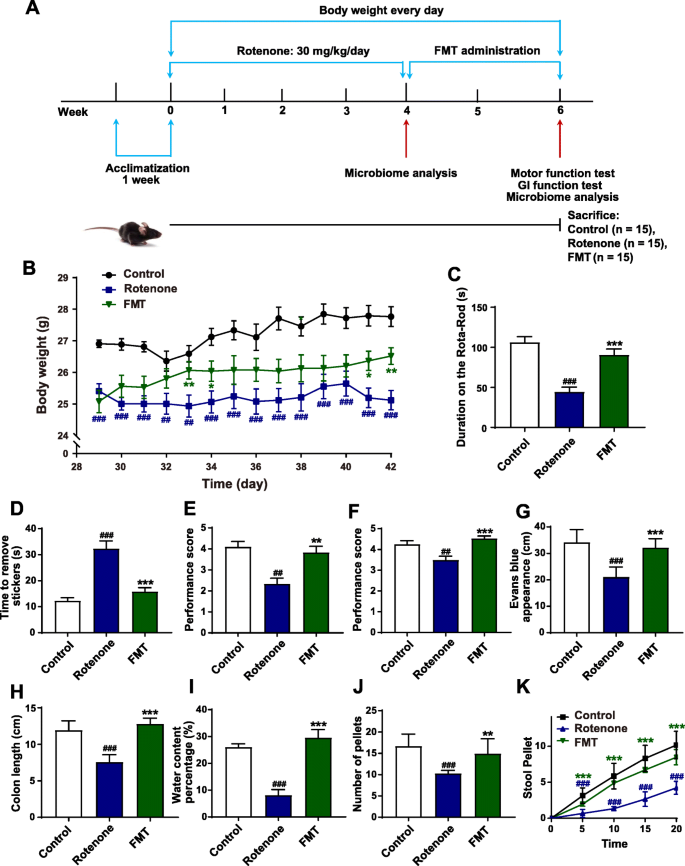
Fecal microbiota transplantation protects rotenone-induced Parkinson's disease mice via suppressing inflammation mediated by the lipopolysaccharide-TLR4 signaling pathway through the microbiota-gut-brain axis, Microbiome

Gut Microbiota Regulate Motor Deficits and Neuroinflammation in a Model of Parkinson's Disease - ScienceDirect
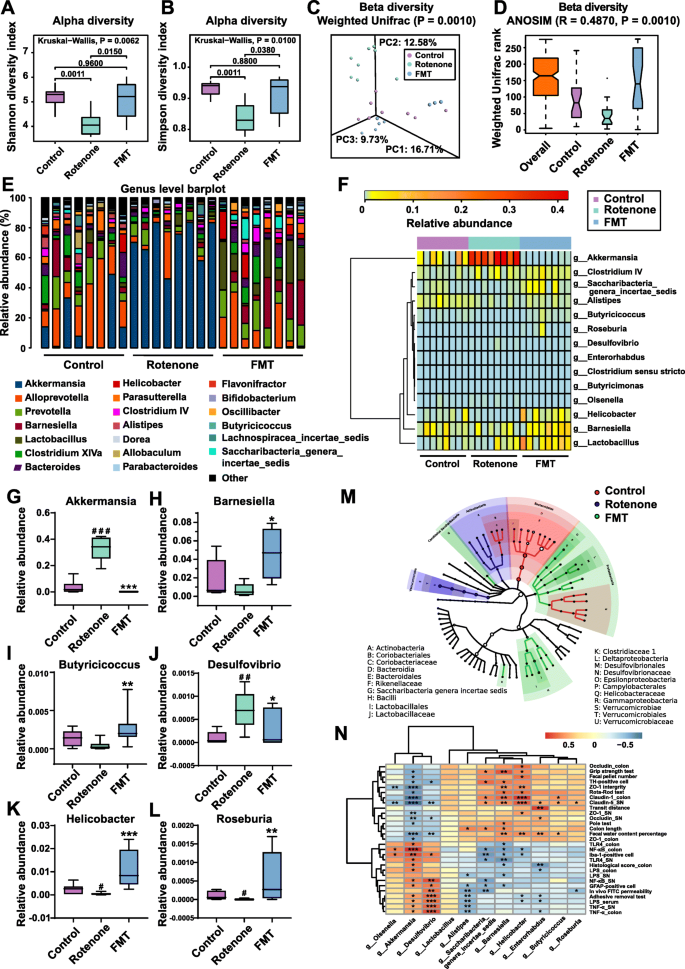
Fecal microbiota transplantation protects rotenone-induced Parkinson's disease mice via suppressing inflammation mediated by the lipopolysaccharide-TLR4 signaling pathway through the microbiota-gut-brain axis, Microbiome

Gut Microbiota Regulate Motor Deficits and Neuroinflammation in a Model of Parkinson's Disease - ScienceDirect

PDF) Fiber deprivation and microbiome-borne curli shift gut bacterial populations and accelerate disease in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease

Possible Signaling Pathways in the Gut Microbiota–Brain Axis for the Development of Parkinson's Disease Caused by Chronic Consumption of Food Additives
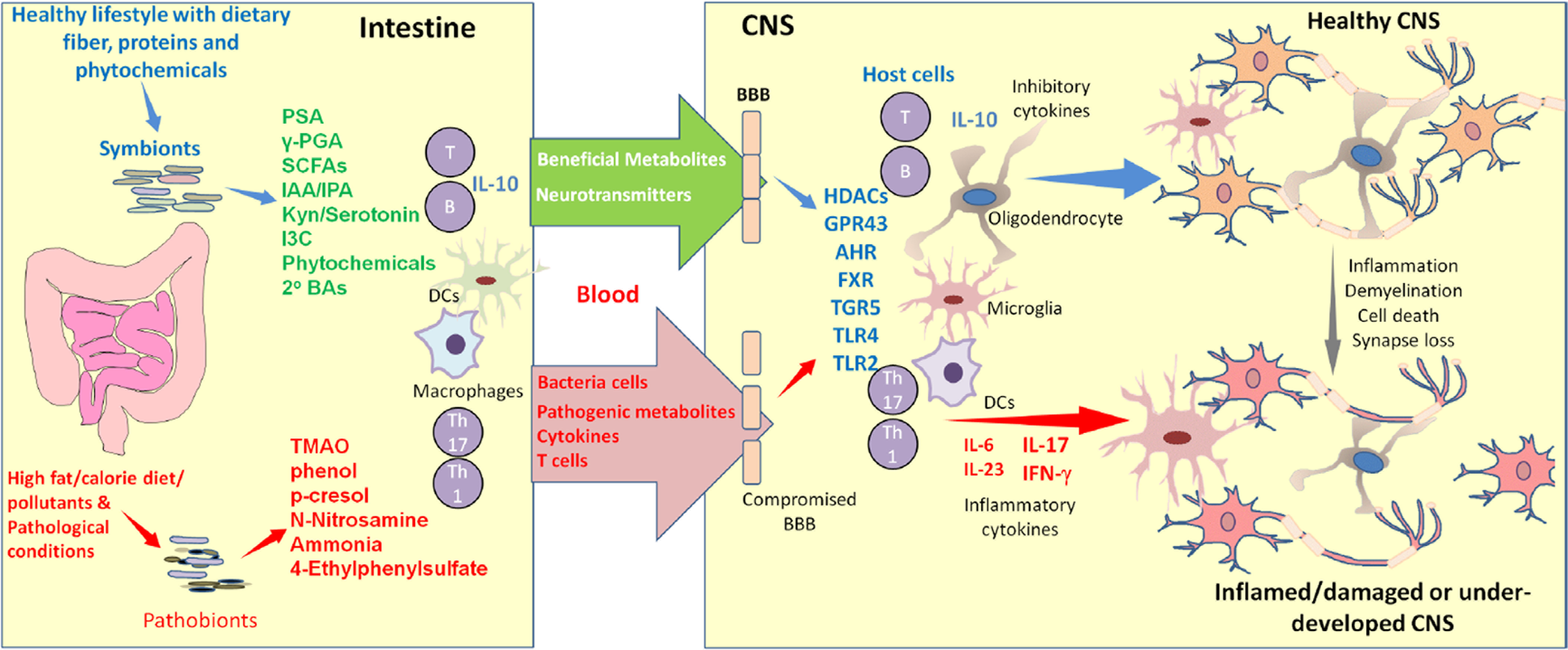
Regulation of common neurological disorders by gut microbial metabolites

Implications of the Human Gut–Brain and Gut–Cancer Axes for Future Nanomedicine

Fiber deprivation and microbiome-borne curli shift gut bacterial populations and accelerate disease in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease - ScienceDirect

Gut Microbiota Regulate Motor Deficits and Neuroinflammation in a Model of Parkinson's Disease - ScienceDirect
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)